Candy sorter
Sorts candies based on their colour.
Author: Sândulache Mihnea-Ștefan
GitHub Project Link: https://github.com/UPB-PMRust-Students/proiect-mihneasandulache
Description
A device which uses a colour sensor in order to sort candies based on their colours. The identified colour is then displayed on a LCD screen and a LED is turned on corresponding with the respective colour.
-
The system utilizes a sensor to identify colour of the candy.
-
The pipe is rotated to a pre-calculated angle, based on the colour of the candy so it drops in a special glass.
-
A servomotor then rotates the bottom side of the earrings box and the candy drops into an improvised funnel through the pipe and into the correct glass.
-
The LCD screen showcases the colour of the candy.
-
LEDs are then turned on based on the colour.
-
Both servomotors rotated back to their initial state and another candy is ready to be dropped.
Motivation
This project reflects my desire to dive deeper into embedded programming using a new language — Rust. I chose Rust for its performance and safety, and because it's becoming a strong player in the embedded world.
As a kid, I was fascinated by M&M’s candy dispensers and often imagined building one that could sort candies by flavour or color. That idea stuck with me and inspired this project.
While planning the system, from sensors to microcontrollers, I realized it’s more than just code. It’s also about designing and building the physical device, something that taps into my love for arts and crafts.
Architecture
The Raspberry Pi Pico 2W serves as the central control unit, directing and managing all other components utilized within the project.
The LCD serves as an interface for showcasing the colour of the candy, it is connected to the Pico through I2C
The servomotors are responsible for rotating the candy and the pipe, ensuring that the candy is dropped into the correct glass.
The LED lights up in the corresponding colour of the candy, providing a visual indication of the detected colour.
The colour sensor identifies the colour of the candy and sends the data to the Pico for processing.
The pipe is rotated to a pre-calculated angle based on the colour of the candy, ensuring it drops into the correct glass.
The earrings box is used to create a makeshift arm, which is rotated by the servomotor. This arm is responsible for holding the candy and dropping it into the correct glass.
Log
Week 5 - 11 May
I started the project by gathering all the necessary components and setting up the Raspberry Pi Pico 2W. I also began researching the TCS230 colour sensor and how to interface it with the Pico. After that, I began wiring all the components together, testing the connections, then hit a really rough blockage with the LCD display. I was unable to get it to work, so I decided to use a different one, the 1602 LCD with I2C interface. After searching the internet for hours trying to find a crate, I finally found one that worked.
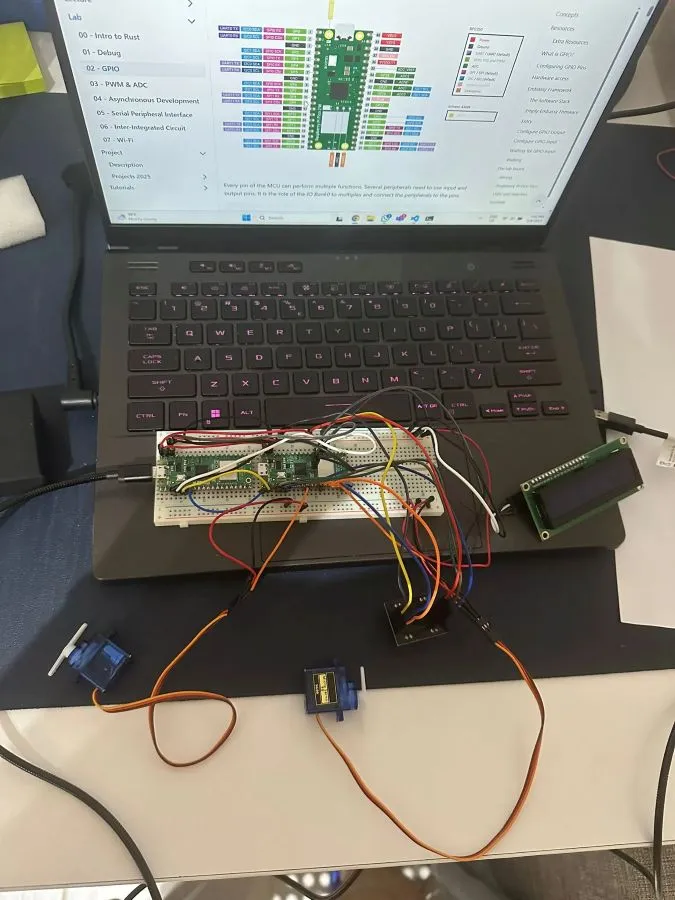
Week 12 - 18 May
Began putting all the pieces into place and designed the structure of the funnel and the way the candy will be dropped. The code is almost done, I just need to calibrate the angles of the servomotors and the color sensor to better recognise the colors. I am also attaching a drive link to a video of the candy sorter in action which is almost complete software-wise.
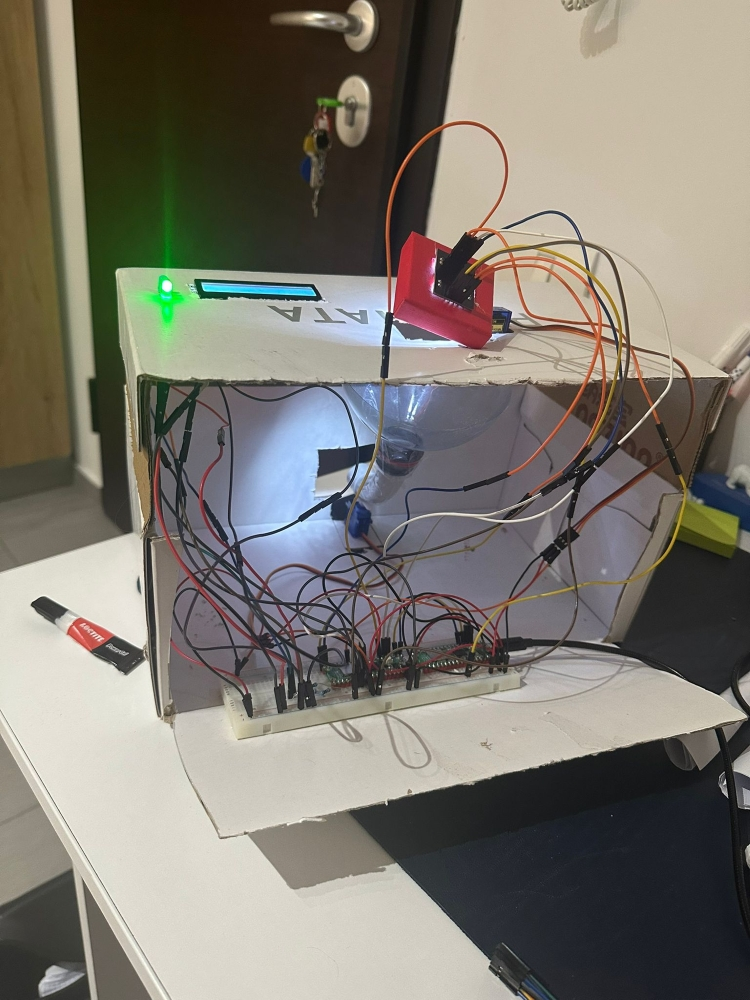
Week 19 - 25 May
Finished the code by calibrating the color sensor. Since the sensor was not accurately detecting the green color, I decided to change it into yellow since I had some extra yellow candies left. I also added some extra messages on the LCD so the user knows when to drop the candy. Here is a video of the final product in action.
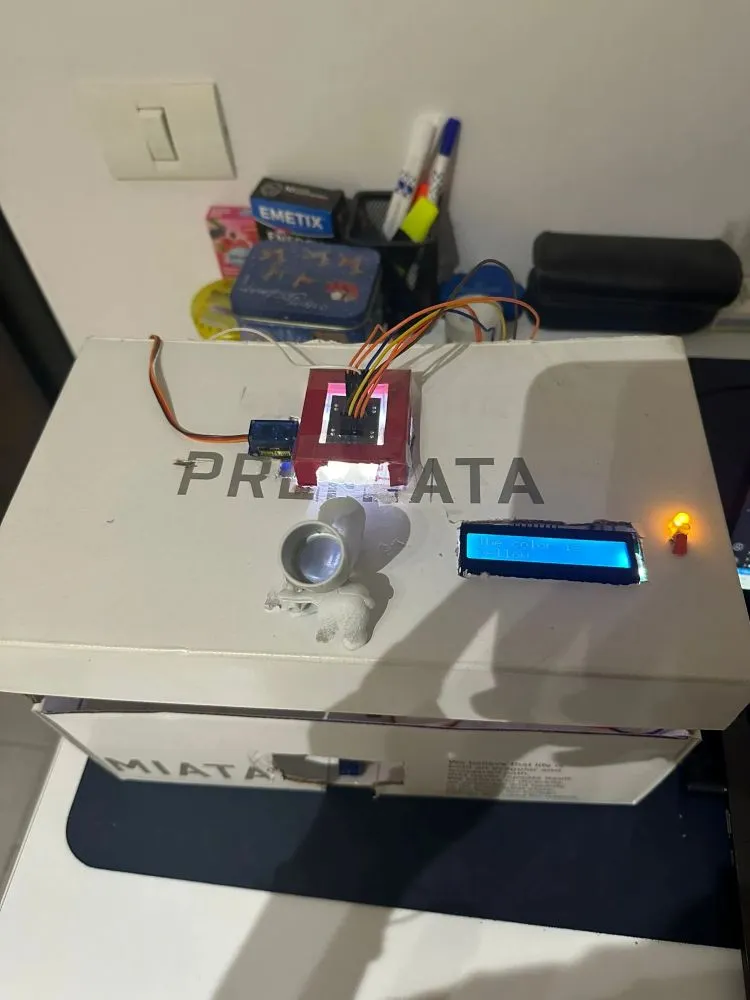

Hardware
- Raspberry Pi Pico 2W:
- Purpose: Controls all components.
- Function: Acts as the main controller, coordinating the operations of sensors, motors, buzzers, and the LCD display.
- Colour Sensor:
- Purpose: Detects the colour of the candy.
- Function: Identifies the colour of the candy and sends the data to the Raspberry Pi Pico for processing.
- LCD Display:
- Purpose: Displays the detected colour of the candy.
- Function: Provides a visual interface for the user, showing the colour of the candy detected by the sensor.
- Servomotor:
- Purpose: Rotates the candy and the pipe.
- Function: Controls the movement of the candy and the pipe, ensuring that the candy is dropped into the correct glass.
- LED:
- Purpose: Provides a visual indication of the detected colour.
- Function: Lights up in the corresponding colour of the candy, providing a visual indication of the detected colour.
Hardware Overview:
- The Raspberry Pi Pico controls and coordinates all components.
- The LCD displays the detected colour of the candy.
- The servomotors rotate the candy and the pipe, ensuring that the candy is dropped into the correct glass.
- The LED lights up in the corresponding colour of the candy.
- The colour sensor identifies the colour of the candy and sends the data to the Pico for processing.
Schematics
Bill of Materials
| Device | Usage | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Rapspberry Pi Pico 2W | The microcontroller | 39,66 RON |
| TCS230 | Colour Sensor | 38,99 RON |
| 1602 LCD with I2C Interface | LCD Display | 16,34 RON |
| Servomotor | Servomotor | 14 RON |
Software
| Library | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| embassy-rp | RP2350 Peripherals | Used for accessing the peripherals |
| embedded-hal | Embedded Hardware Abstraction Layer | Used for accessing the hardware |
| lcd1602-diver | LCD display | Used for controlling the LCD display |
| cortex-m | Provides low-level APIs for ARM Cortex-M processors | Interrupt handling and system control |
| embassy-executor | Asynchronous executor for embedded systems | Used for managing tasks and scheduling |
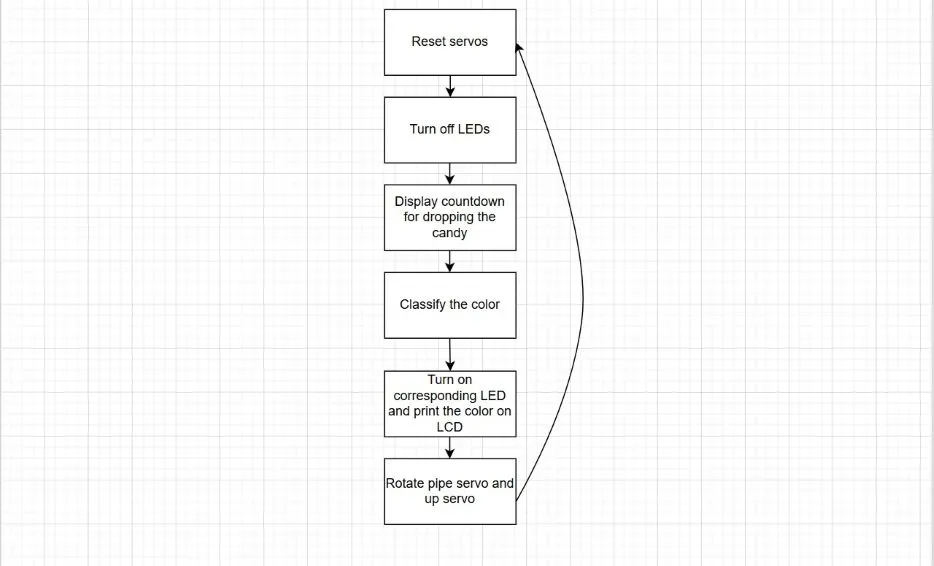
The general flow of the programme is the following: drop the candy under the TCS230 color sensor, wait for the candy to set still. The sensor reads the frequency of each color component (red, green, blue) and uses these values to do an euclidean distance between the current reading and 3 reference readings, which have been previously calculated averaging 5 readings for each candy color.
The color with the smallest distance is the one considered the candy to be. A message is printed on the LCD screen and an LED is turned on to indicate the color of the candy. Meanwhile, the two servomotors rotate accordingly and let the candy drop. After 2 seconds, the servos return to their initial position, the screen is cleared and the LEDs are turned off and the process can be repeated.